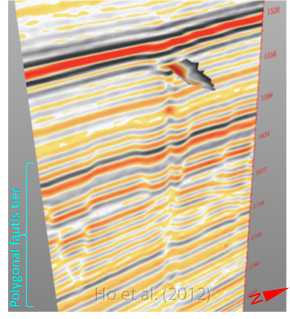
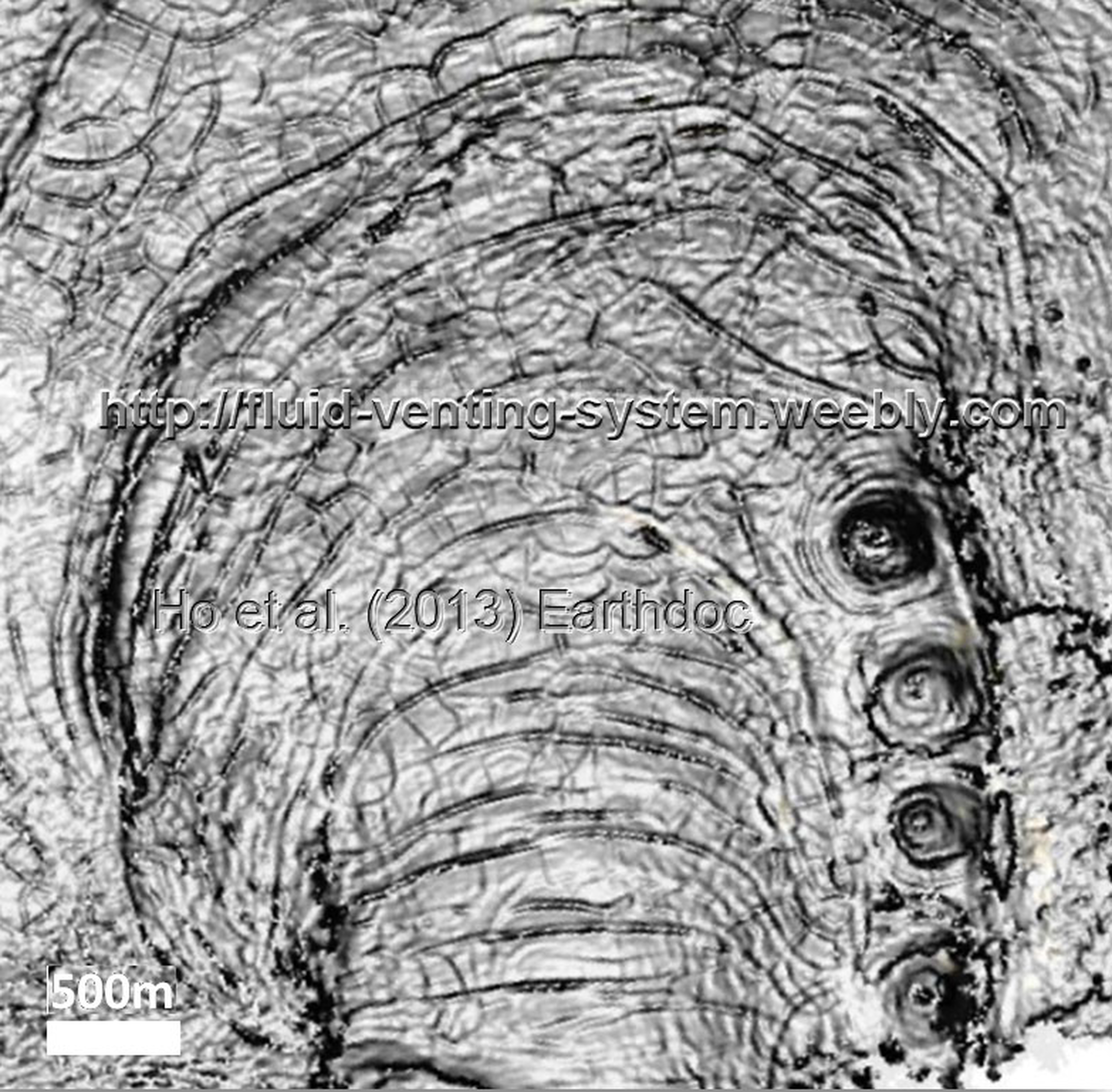
Key words: Sutieng Ho pockmark Sutieng Ho gas chimney seismic Sutieng Ho polygonal fault Sutieng Ho methane authigenic carbonate Sutieng Ho Lower Congo Basin Angola
Interactions between linear chimneys, pockmarks and polygonal fault systems
Fluid venting structures are the expression of hydrocarbon leakage or other type of fluid expulsion in sub-surface marine sediments.
Hydrocarbon venting structures are often associated with faults and fractures which provide pathways for fluid migration through the subsurface (Ligtenberg, 2005). The expression of fluid flow structures have been observed on seismic refection data for the last three decades and have become an object of interest in marine geology. Much scientific research has focused on the relationship between faults and fractures and fluid venting structures. However, the interactions between fluid venting structures and strata-bound arrays of compaction-related normal faults (discovered by Henriet et al., 1982) known as “polygonal faults” (Cartwright and Lonergan, 1996) have only been studied closely in the last decade and remain poorly understood.
In this research, we document several types of new fluid venting structures Offshore Angola that associated with polygonal faults. In particular, this work attempts to explain mechanisms by which fluid venting structures form and establish their link with polygonal faults.
You can use the links below to access our publications on this topic.

Fluid-Venting-System website by S. HO is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.