Photo Album of Mud Volcanoes in Azerbaijan
- by Martin Hovland
"Mud volcanoes are some of the world's most dynamic and statically unstable clastic features. We define a mud volcano as a positive topographical feature constructed mainly of mud, and other sedimentary constituents, which periodically or continuously vents liquid mud, including water, oil, and gas." - Hovland et al. (1997).
On Dasgil mud volcano (Azerbaijan), there are two types of vents, this one, which is a 'Salse', characterized by having no rim, and where salt water flows from below (salty water does not transport clay, as it flocculates). The other type (not shown here), is the 'Gryphon' where fresh (condensation) water flows from below, and which transports clay to the surface, producing the characteristic bubbling clay pots (Gryphons).
Photographed by Boris from Baku in 1995.
Photographed by Boris from Baku in 1995.
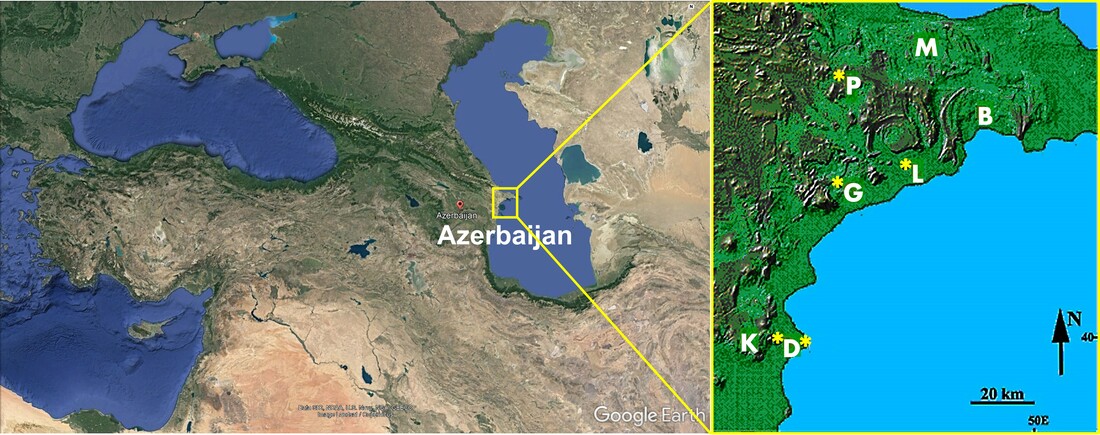
This photo album includes pictures of mud volcanoes at Garadagh, Lake Masasyr-Gel, Lokbatan, Dashgil, Kotyrdag and Perigishgyl.
The locations of the outcrops are indicated by letters on the map below.
The locations of the outcrops are indicated by letters on the map below.
Please click the button below to view the photos.
References in this album
Hovland, M., Hill, A., & Stokes, D. (1997). The structure and geomorphology of the Dashgil mud volcano, Azerbaijan. Geomorphology, 21(1), 1-15.
Planke, S., Svensen, H., Hovland, M., Banks, D. A., & Jamtveit, B. (2003). Mud and fluid migration in active mud volcanoes in Azerbaijan. Geo-Marine Letters, 23(3-4), 258-268.
Hovland, M., Hill, A., & Stokes, D. (1997). The structure and geomorphology of the Dashgil mud volcano, Azerbaijan. Geomorphology, 21(1), 1-15.
Planke, S., Svensen, H., Hovland, M., Banks, D. A., & Jamtveit, B. (2003). Mud and fluid migration in active mud volcanoes in Azerbaijan. Geo-Marine Letters, 23(3-4), 258-268.